Hardware
End devices:
- CPU
- RAM
- Motherboard
- Storage
- Operating system
- Apps
We need a wireless or a wired Network interface card (NIC)
If it is wired we will need a cable which is usually a ethernet or RJ45.
Interconnection devices:
- Switches, Connects devices together (clever).
- Routers, connects devices to Wi-Fi.
- Modems, device used by computers to transmit data.
- Hub, Connects devices together (stupid).
- Wireless access point (WAP), Connects things wirelessly.
- Bridge, connects two or more networks.
- Repeater, boosts signals over long distances.
Neil notes
Thursday, 29 January 2015
Thursday, 8 January 2015
Protocols
Protocols
Ethernet, HTTP, TCP/IP, FTP, DHCP, DNS, SMTP.
we need standard 'languages' for devices and software to communicate.
Ethernet (fast ethernet, gigethernet) - R345, Cat5, CatSE, Cat6.
10mbps 100mbps 1000mbps cables
The most used network protocol for cables.
TCP/IP (Transmission control protocol, internet protocol)
The most used network protocol for network communication.
HTTP (Hypertext transfer protocol) HTTPS (secure)
The standard protocol for websites (downloading content content from a web server)
DNS (Domain name service)
Link the host name to the IP address. Either a host name on a network or a website.
FTP (File transfer protocol)
Used for downloading and uploading files.
SMTP (Simple mail transfer protocol)
Used for email.
DHCP (Dynamic host configuration protocol)
A server or router supplies IP addresses to any device.
IPs have a lease time.
Used for dynamic addressing.
Addresses can also be static - they are set manually and they don't change.
The static address has to be in the same address range as the other devices.
Mainly for servers and printers.
Ethernet, HTTP, TCP/IP, FTP, DHCP, DNS, SMTP.
we need standard 'languages' for devices and software to communicate.
Ethernet (fast ethernet, gigethernet) - R345, Cat5, CatSE, Cat6.
10mbps 100mbps 1000mbps cables
The most used network protocol for cables.
TCP/IP (Transmission control protocol, internet protocol)
The most used network protocol for network communication.
HTTP (Hypertext transfer protocol) HTTPS (secure)
The standard protocol for websites (downloading content content from a web server)
DNS (Domain name service)
Link the host name to the IP address. Either a host name on a network or a website.
FTP (File transfer protocol)
Used for downloading and uploading files.
SMTP (Simple mail transfer protocol)
Used for email.
DHCP (Dynamic host configuration protocol)
A server or router supplies IP addresses to any device.
IPs have a lease time.
Used for dynamic addressing.
Addresses can also be static - they are set manually and they don't change.
The static address has to be in the same address range as the other devices.
Mainly for servers and printers.
Topologies
there are 3 fundamental simple physical topologie shapes:
Single cable connects all the systems together.
There are terminators at the ends to bounce the signal back and forth.
Advantages: small, inexpensive and easy to expand.
Disadvantages: high maintenance costs.
Ring
each node is connected to the two nearest nodes to create a ring.
Advantages: easier to manage and find defective nodes, reliable communication, handles high network traffic, well suited for transmitting over long distance on a LAN.
Disadvantages: expensive, uses a lot of cable, not as widely used so there are fewer setup options.
Star
Every node is connected through a central device.
Any single cable only connects two devices.
Requires the most cable.
Easy to expand the network.
Advantages: low start up costs, easy to manage, scale able, most common.
Disadvantaged: uses the most cable out of the three.
- Bus
- Ring
- Star
Single cable connects all the systems together.
There are terminators at the ends to bounce the signal back and forth.
Advantages: small, inexpensive and easy to expand.
Disadvantages: high maintenance costs.
Ring
each node is connected to the two nearest nodes to create a ring.
Advantages: easier to manage and find defective nodes, reliable communication, handles high network traffic, well suited for transmitting over long distance on a LAN.
Disadvantages: expensive, uses a lot of cable, not as widely used so there are fewer setup options.
Star
Every node is connected through a central device.
Any single cable only connects two devices.
Requires the most cable.
Easy to expand the network.
Advantages: low start up costs, easy to manage, scale able, most common.
Disadvantaged: uses the most cable out of the three.
Thursday, 2 October 2014
Utilities
Utilities
- Keep your computer running smoothly
-Security
-Anti-malware
-Anti-virus (detect and delete viruses which are updated regularly and new viruses are made everyday)
-Anti-spyware - trying to get files, personal information (key logging)
-Pop-up blocker
-Firewall
-Allows good traffic and stops bad.
-Formatting
-Gets your drive ready for files.
-File structure
-Defragmentation
-Put broken up files back together.
-Speeds up machine, creates space.
-Internet-open a webpage
-Downloads, cookies, images, text, ads, videos, music, games, etc. All stored on your hard drive and builds up overtime, takes up space and slows your computer down.
-Cookies
-Stores details of your visit to the website like preferences and passwords.
Temp System Files
Temporary system files are created constantly and need to be deleted.
- Keep your computer running smoothly
-Security
-Anti-malware
-Anti-virus (detect and delete viruses which are updated regularly and new viruses are made everyday)
-Anti-spyware - trying to get files, personal information (key logging)
-Pop-up blocker
-Firewall
-Allows good traffic and stops bad.
-Formatting
-Gets your drive ready for files.
-File structure
-Defragmentation
-Put broken up files back together.
-Speeds up machine, creates space.
-Internet-open a webpage
-Downloads, cookies, images, text, ads, videos, music, games, etc. All stored on your hard drive and builds up overtime, takes up space and slows your computer down.
-Cookies
-Stores details of your visit to the website like preferences and passwords.
Temp System Files
Temporary system files are created constantly and need to be deleted.
Friday, 19 September 2014
Software
Software
Operating system
Windows (vista, xp, 7, 8, 95, 98) - installed on PC with a license
Linux (Ubuntu, red hat, raspberry OS) - Linux is free and open source
IOS - iphone, tablets, watches
Android - phones, tablets, kindle
Mac OS - Apple Mac
Blackberry OS - blackberry phones, tablets
Unix - specialist machines.
Purpose:
User interacts with the OS and the OS interacts with the Hardware and vice versa.
The OS uses a GUI Graphical User Interface (WIMPS)
CLI - Command Line Interface

This is a diagram of the interactions between the User, Application, OS and Hardware
An operating system is a piece of software which gives the user an interface so they can interact with their hardware through the use of applications. The OS will also allow the user to see information about their hardware. If we do not have an OS then the user will be unable to do anything with their hardware and the money spent on the hardware will have been wasted.
This is a diagram of the interactions between the User, Application, OS and Hardware
An operating system is a piece of software which gives the user an interface so they can interact with their hardware through the use of applications. The OS will also allow the user to see information about their hardware. If we do not have an OS then the user will be unable to do anything with their hardware and the money spent on the hardware will have been wasted.
Applications
applications do everything else.
Thursday, 18 September 2014
BIOS and CMOS
Computer start up order
=>Turn on
=>BIOS (Basic Input/Output System)
-Checking hardware and initializing it
-Show error if some hardware isn't working
-Boots the devices in order.
-ROM chip (Read Only Memory) can't write to it.
=>Boot-up OS HDD
CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor)
-Works together with the BIOS.
-Allows you to change settings because it is writable.
-Stores the date and time, device boot order, etc.
-RAM chip so it has working memory, if power is cut the settings are lost. To prevent this there is a battery which keeps the CMOS from losing power and forgetting the changes. The battery charges while the computer is on.
Peripheral devices
a device that plugs into the outside of the computer
examples:
-keyboard (input)
-mouse (input)
-headphones (output)
-usb (input and output)
-monitor (output)
-microphone (input)
Peripheral devices
a device that plugs into the outside of the computer
examples:
-keyboard (input)
-mouse (input)
-headphones (output)
-usb (input and output)
-monitor (output)
-microphone (input)
Friday, 12 September 2014
PC components
Unit 2 Notes
A PC is made up of many different parts:

Motherboard:
Connects all parts of the computer together. AKA System board, Main board.
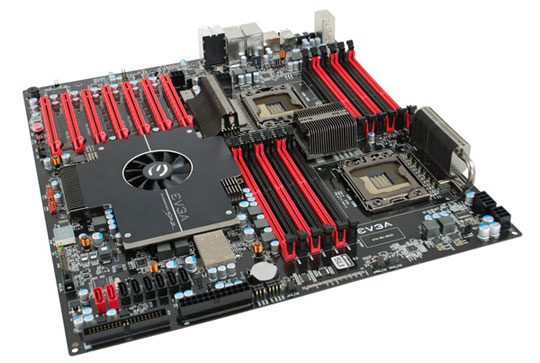
CPU:
The brain of the computer. Stands for Central Processing Unit
-Multicore: more than one core in the space.
-Hyper-threading: allows multiple threads to be used alongside each other.
-Speed in GHz
-Multicore: more than one core in the space.
-Hyper-threading: allows multiple threads to be used alongside each other.
-Speed in GHz

RAM:
The working memory/short term memory of the computer. It stands for Random Access Memory.
When you shut the power down anything on the RAM gets wiped.
Examples of RAM:
SIMM- Single In-line Memory Module, teeth are only on one side.
DIMM- Dual In-line Memory Module, teeth are on both side.
DDR- Double Data Rate.
DDR2- Double Data Rate, bigger and faster than DDR.
DDR3- Double Data Rate, bigger and faster than DDR2.
RAM is measured in size (GB) and a little speed.
When you shut the power down anything on the RAM gets wiped.
Examples of RAM:
SIMM- Single In-line Memory Module, teeth are only on one side.
DIMM- Dual In-line Memory Module, teeth are on both side.
DDR- Double Data Rate.
DDR2- Double Data Rate, bigger and faster than DDR.
DDR3- Double Data Rate, bigger and faster than DDR2.
RAM is measured in size (GB) and a little speed.

Hard Drive:
The long term storage of the computer. AKA HDD (Hard Disk Drive)

GPU:
The graphics card of the PC. Stands for Graphics Processing Unit.

Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
